Coccidiosis in rabbits: treatment, symptoms, prevention, signs of the disease
Coccidiosis in rabbits kept at home for decorative purposes is a rather rare phenomenon. But for their brethren, bred for meat and skin, the disease poses a serious threat.
What is the danger of coccidiosis of rabbits
These animals are susceptible to many infectious diseases. The greatest damage is caused by viral diseases of rabbits. So, one of the diseases that sharply reduce the efficiency of raising animals is coccidiosis (eimeriosis). When kept on litter, the invasion spreads very quickly and affects the entire rabbitry. The existing drugs are sufficiently effective both for treatment and prevention of the disease, but they are very expensive. A recovered animal is forever behind in growth and development. In addition, coccidiosis in rabbits can occur in a latent form and provoke a decrease in resistance to other diseases, as well as contribute to poor digestibility of feed. As a result, food consumption increases while body weight gain remains below average.

Therefore, the basis of successful rearing is measures to prevent coccidiosis in rabbits (after all, treatment is always more expensive than prevention). The economic damage from product shortfalls during an outbreak of eimeriosis is enormous. If we consider parasitic diseases of rabbits, coccidiosis is the most dangerous invasion, since it is characterized by a high level of morbidity, and if untreated, mortality can reach 100%.
Causes of the disease
Coccidiosis in rabbits is caused by nine types of eimeria. These are the simplest unicellular organisms belonging to the order of coccidia. They have a complex developmental cycle, thanks to which the parasite is highly reproducible. It has been established that one sick animal daily excretes from 9 to 680 million coccidial oocysts into the external environment. And from one oocyst, several million eimeria develop. Another feature of the parasite is that each species has a strict specificity. Therefore, despite the fact that all classes of animals suffer from coccidiosis, rabbits can only get infected from rabbits, chickens - only from chickens, sheep - only from sheep, and so on.
Recommended
How many months can a boy be seated and should it be done
More recently, the baby was born. He was so small and completely helpless. But now he has learned to hold his head, smile, hold toys with his hands. And the parents begin to think: how many months can a boy be seated? I wish he could look at the worl...
Lessons of a happy childhood: trampolines for children with a net
For children, their whole life is about movement. They like to run, jump, and arrange various competitions. That's why they are so reluctant to go to the country with adults or get bored when they are at home. But this state of affairs is very easy t...
Curtains in the nursery for a girl. How to make the right choice?
The children's room is a separate world in which the child lives. Since he spends a lot of time there, parents should take the issue of interior design very seriously, paying attention to every detail. In this article we will talk about how to choose...
The complexity of the treatment and prevention of invasion is that coccidia are ubiquitous, and the infection of rabbits with eimeria ranges from 70-100%. Sick and recovered animals, adult parasitic rabbits secrete spore forms of the pathogen (oocysts) with feces into the external environment. It is almost impossible to destroy this form of the pathogen, since the spore is very resistant to the effects of chemical and physical factors. Oocysts are transferred on the soles of shoes, with equipment, and contaminate walking yards. In addition, rabbits are designed so that eating their own feces is an integral part of their healthy digestion. Night droppings excreted from the cecum (light soft balls covered with mucus) are a source of B vitamins, stimulate immunity, and supply the necessary microflora to the intestines. Unfortunately, along with droppings, eggs of coccidia enter the body.
Poor conditions for rearing young animals are of great importance in the occurrence of the disease: unsanitary conditions, overcrowding, high humidity, temperature fluctuations in the room, the formation of different age groups of animals, poor quality feed, a sharp change in diet. Outbreaks of coccidiosis often occur in the spring and autumn periods, but they can occur at any time of the year.
Characteristics of the causative agent of the disease
Five types of coccidia are of practical importance. Four of them parasitize in the epithelium of the small and large intestine: E. perforans, E. media, E. magna, E. irresidua. The fifth species, E. stiedae, lives in the epithelium of the liver bile ducts. In the contents of the intestine or in the droppings, a small number of oocysts (1-2 per field of view) may normally be contained. This does not mean there is a disease. In some cases, other viral or parasitic diseases of rabbits can show intestinal symptoms. A photo taken under a high magnification microscope allows a good look at the structure of the coccidial oocysts. They are oval or round formations ranging in size from 10 to 40 microns, a double membrane and dark contents (sporocyst) are well marked. At one tapered end there is a small cap (micropile). The diagnosis of coccidiosis in rabbits is confirmed by examination of fecal matter under a microscope using the Darling method. Detection of single oocysts in the absence of other symptoms of the disease is not a basis for the diagnosis.
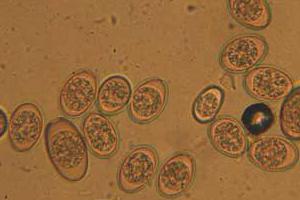
Clinical signs of coccidiosis
This ailment can occur in acute, subacute and chronic forms. Young animals aged 20 to 60 days are most susceptible to the disease. Often, coccidiosis manifests itself during the period of weaning of rabbits from the mother and when they are transferred to regular feed. In animals 3-5 months of age, the disease is less severe, and adult rabbits are practically not susceptible to disease, although they can be carriers and provoke coccidiosis. Symptoms appear 4-12 days after infection. Theoretically, they separate intestinal, hepatic and mixed forms of coccidiosis, but in practice, the invasion proceeds mainly in a mixed form. First, the intestines are affected, along with general signs of malaise (lethargy, lack of appetite), diarrhea appears, less often constipation, the abdomen becomes swollen and painful, the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth turn pale. Sick animals lose weight, stunted, mucus and bloody inclusions are found in the feces.

The appearance of feces helps diagnose coccidiosis and other parasitic diseases of rabbits. A photo of droppings with coccidiosis clearly shows characteristic streaks of red or orange.
Often sick animals have rhinitis and conjunctivitis, and saliva production increases. With liver damage, yellowness of the mucous membranes appears, sometimes paralysis of the limbs and convulsions occur. The abdomen greatly increases in volume, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) may develop. If untreated, rabbits usually die on the 7-10th day.
When opened, they reveal pallor of the mucous membranes, yellowness, inflammation in the intestines (the walls are thickened, the contents with blood, the mucous membrane peels off with a "stocking" or with foci of necrosis , pityriasis bloom). On the outside, the shell of the intestinal wall is gray, dotted with whitish, small foci dense to the touch. In the liver, characteristic lesions are clearly visible: along the bile ducts, off-white or yellowish nodules the size of a grain or even a pea, not isolated from the surrounding tissues. In severe cases, lesions affect the liver parenchyma.
How to distinguish coccidiosis from other diseases
Intestinal symptoms are characteristic of other diseases of rabbits. The detection of a significant number of oocysts in the litter allows the diagnosis of coccidiosis. The symptoms described above confirm the presence of this disease and are an indication for treatment. It is carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian, comprehensive measures are taken to destroy the pathogen in the body, remove intoxication and maintain electrolyte balance. Since there are various diseases in rabbits, the symptoms and treatment for each will vary. It is important to correctly and timely make the correct diagnosis. In each case, it is necessary to carry out a differential analysis, since clear, characteristic symptoms of the disease are not always present. Signs of intestinal damage are manifested by the following diseases of rabbits:
- Coccidiosis - detection of oocysts in the droppings, blood inclusions, the characteristic age of the animal.
- Enterotoxemia - an acute course, the presence of a large amount of gases in the droppings ... Age 8-30 days. Detection of the causative agent - bacteria C. perfringens.
- This ailment can occur in acute, subacute and chronic forms. Young animals aged 20 to 60 days are most susceptible to the disease. Often, coccidiosis manifests itself during the period of weaning of rabbits from the mother and when they are transferred to regular feed. In animals 3-5 months of age, the disease is less severe, and adult rabbits are practically not susceptible to disease, although they can be carriers and provoke coccidiosis. Symptoms appear 4-12 days after infection. Theoretically, they separate intestinal, hepatic and mixed forms of coccidiosis, but in practice, the invasion proceeds mainly in a mixed form. First, the intestines are affected, along with general signs of malaise (lethargy, lack of appetite), diarrhea appears, less often constipation, the abdomen becomes swollen and painful, the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth turn pale. Sick animals lose weight, stunted, mucus and bloody inclusions are found in the feces.

The appearance of feces helps diagnose coccidiosis and other parasitic diseases of rabbits. A photo of droppings with coccidiosis clearly shows characteristic streaks of red or orange.
Often sick animals have rhinitis and conjunctivitis, and saliva production increases. With liver damage, yellowness of the mucous membranes appears, sometimes paralysis of the limbs and convulsions occur. The abdomen greatly increases in volume, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) may develop. If untreated, rabbits usually die on the 7-10th day.
When opened, they reveal pallor of the mucous membranes, yellowness, inflammation in the intestines (the walls are thickened, the contents with blood, the mucous membrane peels off with a "stocking" or with foci of necrosis , pityriasis bloom). On the outside, the shell of the intestinal wall is gray, dotted with whitish, small foci dense to the touch. In the liver, characteristic lesions are clearly visible: along the bile ducts, off-white or yellowish nodules the size of a grain or even a pea, not isolated from the surrounding tissues. In severe cases, lesions affect the liver parenchyma.
How to distinguish coccidiosis from other diseases
Intestinal symptoms are characteristic of other diseases of rabbits. The detection of a significant number of oocysts in the litter allows the diagnosis of coccidiosis. The symptoms described above confirm the presence of this disease and are an indication for treatment. It is carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian, comprehensive measures are taken to destroy the pathogen in the body, remove intoxication and maintain electrolyte balance. Since there are various diseases in rabbits, the symptoms and treatment for each will vary. It is important to correctly and timely make the correct diagnosis. In each case, it is necessary to carry out a differential analysis, since clear, characteristic symptoms of the disease are not always present. Signs of intestinal damage are manifested by the following diseases of rabbits:
- Coccidiosis - detection of oocysts in the droppings, blood inclusions, the characteristic age of the animal.
- Enterotoxemia - an acute course, the presence of a large amount of gases in the droppings ... Age 8-30 days. Detection of the causative agent - bacteria C. perfringens.
- Tizzer's disease is an acute course, death 1-2 days after the manifestation of clinical signs. Detection of the causative agent in the feces - bacteria B. piliformis.
- Helminthiasis - no blood in the droppings, chronic course of the disease, detection of worms or their eggs in the feces.
- Infectious enteritis of bacterial origin (colibacillosis, dysentery, enterobacter, proteus) - affect young animals at the age of 6-10 weeks. Yellow or brownish diarrhea, rapid dehydration, increased thirst, a decrease or increase in body temperature. The mucous membranes are pale. The highest mortality is observed in the period from 5 to 9 weeks.
Coccidiosis in rabbits: treatment
As a therapy, veterinarians prescribe antibacterial drugs of a wide spectrum of action, including number, and anti-coccidial effect. Among them:
- Sulfonamides ("Sulfaquinoxaline", "Sulfachloropyrazine") - in feed and drinking water. The recommended dose is 0.1 g per 1 kg of live weight. At the same time, "Monomycin" is prescribed at a dose of 25 thousand units/kg of body weight. Two five-day courses are carried out with an interval of three days.
- Nitrofurans ("Nitrofurazone"). The dosage is 1-1.5 g per 1 kg of live weight.
Fermented milk products are included in the diet: milk whey at a dose of 25-30 ml per head, yogurt, ABA.

Coccidiostatics in rabbit breeding
Such drugs have a certain toxicity and are quite expensive to manufacture, but have an excellent therapeutic and prophylactic effect. For therapeutic purposes, it is advisable to use them with water, and for prevention, they are mixed into premixes and given with feed. When a diagnosis of coccidiosis is made, treatment is carried out with one of the following drugs (according to the active ingredient):
- Diclazuril ("Solicox", "Diakox").
- Amprolium ("Brovitakoccid", "Koktsidiovit").
- Totlazuril ("Baykoks", "Koktsiprodin", "Stop-coccid").
The dosage of the drug depends on the concentration of the type of active substance. On average, a liquid form of a coccidiostatic is produced in 2.5-5% concentration and given to animals with water at the rate of 10 mg of DV per 1 kg of live weight for 2-3 days in a row. For preventive purposes, the dose is reduced by half, and the course is carried out a little longer. As part of the premix, coccidiostatics are introduced into the feed at a dose of 0.1% and fed during critical periods (change of feed, transfer to another room, weaning of rabbits). Ready-made mixtures can be purchased on the feed market and in veterinary pharmacies. In any case, carefully read the instructions and find out if the drug can be used specifically for rabbits. If the number of animals is small, and coccidiosis is found in rabbits, treatment is carried out by individual administration of the medicine. It is injected into the mouth using a syringe without a needle. Rabbits (the photo given in the article demonstrates how to fix the head correctly) are placed on the table, pressed against the back, preventing the animal from fighting back with its hind legs. The liquid is gently injected into the corner of the mouth behind the lip.
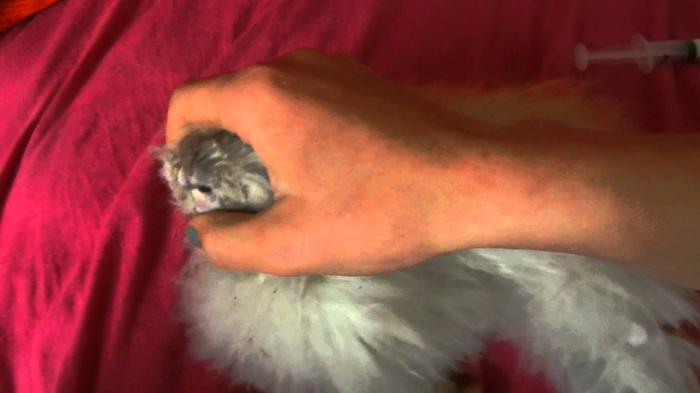 Do not give more than 1 ml of liquid at a time.
Do not give more than 1 ml of liquid at a time.
Prevention of coccidiosis in rabbits
Particular attention is paid to the correct organization of the growing technology. The incidence directly depends on the conditions in which the decorative rabbit is kept. Vaccinations do not always save even from viral diseases. The main way to prevent ailments is to comply with zoohygienic requirements. Prevention of a disease such as coccidiosis in rabbits is carried out using the following measures:
- Keeping animals on slatted floors.
- Avoiding crowding, compliance planting (not less than 0.5 sq. m. per animal).
- Keeping animals in dry, well-ventilated rooms.
- Compliance with the temperature regime (rabbits do not tolerate temperatures above 20 ° С).
- Placing cells in the open air or providing them with ventilation at least 3 cubic meters. per 1 kg of live weight per hour.
- Carrying out daily cleaning of droppings from the cages and changing the litter.
- Clean the feeders and drinkers once a day and scald them with boiling water.
Are there vaccines for rabbits? Of course, if you have one decorative rabbit in your apartment, you do not need to be vaccinated. But for those who breed rabbits for their daily bread, the question is very relevant.
Is there a vaccine against coccidiosis?
There is no vaccine against coccidiosis for rabbits today. Although it is possible that with an increase in demand, such a drug will be invented. After all, scientists have managed to create a vaccine against coccidiosis in chickens that meets the modern needs of chicken producers. At present, the prevention of coccidiosis in rabbits is reduced to general measures to prevent infectious and invasive diseases, as well as to the prophylactic administration of coccidiostatic drugs.
Immunity in recovered rabbits remains for life, animals are immune to re-infection. Immunity is non-sterile, which means lifelong carriage of the pathogen in the body. Such a rabbit can easily infect a previously unhealthy individual if concomitant factors (stress, etc.) occur.
Conditions provoking the disease
Often, coccidiosis in rabbits occurs after vaccinations against HBV and myxomatosis. This does not mean that the vaccine is of poor quality, but indicates a latent course of coccidiosis in the herd. Take preventive measures one week before vaccination and you will avoid complications.

When walking on the grass, move the cage periodically to avoid the accumulation of pathogenic organisms in one place. Feeding should be complete, containing 15% coarse fibers and 20% protein. The presence of hay in the diet is mandatory, even if the animals receive a complete feed. Also, constant access to water is necessary, despite the fact that rabbits receive a significant part of the liquid from the grass.
Compliance with the conditions of feeding and maintenance will avoid such an unpleasant ailment as coccidiosis. If, nevertheless, for some reason, an outbreak of the disease occurred, then with a quick diagnosis and the use of effective drugs, the prognosis is favorable. Do not forget to isolate sick animals and clean the cages with disinfectants. If possible, scald all accessible places with boiling water, and burn metal surfaces and equipment with an open flame using a gas torch or blowtorch.
Article in other languages:

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
A gift for children for graduation in kindergarten. Organization of graduation in kindergarten
The day is coming when children have to leave kindergarten and go to school life. Many of them are looking forward to their first graduation, dreaming of going to school. After this day, any child begins to feel like a truly "big...
An iron wedding is how many years of living together?
There is a unique date in family life - an iron wedding. Why unique? Because it's not often you meet a married couple who celebrate 65 years of marriage. A husband and wife who lived to see such an event and stayed together truly ...
Child at 8 months: mode of the day. Feeding a child at 8 months
Is your child finally eight months old? As a loving and caring parent, you just need to know what the baby's day mode should now be and how often you need to eat a baby at that age. The natural diet of a child at 8 months is diffe...
Flanel: what's the fabric? Characteristics, types, application, care
In the cold season, in the innascence naturally the desire of a person to surround himself with soft, cozy, and most importantly, warm tissues. Ideal for this purpose flannel. What's the fabric? The question is perhaps superfluous...
Washing capsules: instructions for use and reviews
Today, laundry capsules are in high demand and popularity. That's because they've proven themselves in the process. Even the dirtiest things, sewn from different fabrics, become perfectly clean after the first wash. This result ca...
Baby anti-reflux mixtures. How to choose an anti-reflux mixture for a newborn
Being on a mixed diet, infants can often ress before feeding. To prevent this from happening, pediatric doctors recommend the use of special mixtures, which are different depending on the type of thickener.Anti-reflux mixtureAntir...





















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!